WSE-7056 EzRun ClearNative
Purpose and Application
- Buffer for HR-CN-PAGE (High-Resolution Clear Native PAGE)
Features
-
A set of 5× concentrated cathode and anode electrophoresis buffers
-
Simply dilute 5-fold with distilled water before use
-
Does not inhibit enzyme activity or protein functionality
-
Enables HR-CN-PAGE with SDS-free Tris-Glycine polyacrylamide gels
Data
Protocol
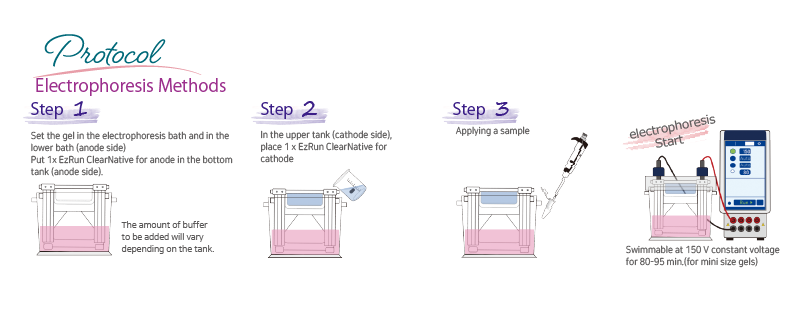
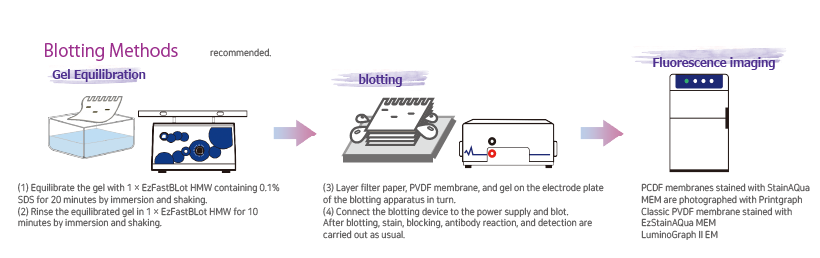
The required buffer volume may vary depending on the electrophoresis tank. Please refer to the table below.
| Gel | Electrophoresis Apparatus | Buffer volume |
|---|---|---|
| Mini size | AE-6530, WSE-1150 | Cathode: 75 mL |
| Anode: 250 mL | ||
| WSE-1165 | Cathode: 250 mL | |
| Anode: 250 mL | ||
| Compact size | WSE-1030, WSE-1040 | Cathode: 135 mL |
| Anode: 110 mL | ||
| Wide size | WSE-1170 | Cathode: 400 mL |
| Anode: 400 mL |
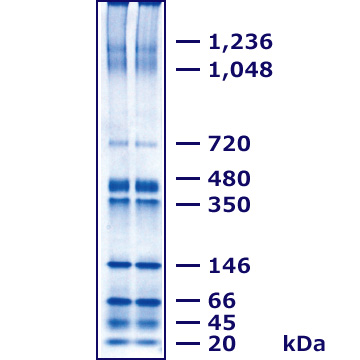
Comparison with conventional Bis-Tris gel methods
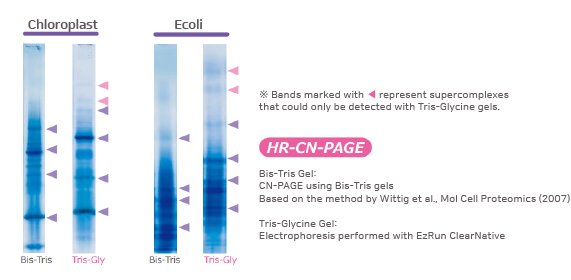
The figure above shows the results of CN-PAGE performed with a self-prepared Bis-Tris gel (according to Schägger et al., 2008) compared with the results of HR-CN-PAGE carried out using the Tris-Glycine gel UH-T310. HR-CN-PAGE was originally developed based on Bis-Tris gels and was not suitable for Tris-Glycine gels. EzRun ClearNative enables HR-CN-PAGE to be performed on Tris-Glycine polyacrylamide gels while maintaining correlation with the electrophoresis patterns obtained using Bis-Tris gels.
Protein activity staining

The figure above shows the results of β-galactosidase activity staining after electrophoretic separation using HR-CN-PAGE, conventional Native PAGE, and SDS-PAGE, captured with the Printgraph Classic. HR-CN-PAGE, like conventional Native PAGE, allows detection without inhibiting enzyme activity. In contrast, SDS-PAGE does not produce detectable bands because SDS affects enzyme activity.
ATTO Native Electrophoresis Buffer Features
| WSE-7056 EzRun ClearNative | WSE-7057 EzRun BlueNative | WSE-7055 EzRun TG | WSE-7066 EzRun MOPS non-SDS |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein denaturation | Non-denaturing (CN-PAGE) | Non-denaturing (BN-PAGE) | Non-denaturing (Native PAGE) | Non-denaturing (Native PAGE) |
| DNA electrophoresis | Not applicable | Not applicable | Compatible with Tris/Glycine agarose gels (Not for RNA) | Compatible with Tris/Glycine agarose gels (Not for RNA) |
| Electrode buffer system | Tris-HCl, Tris/Glycine, amino acid buffers | Tris-HCl, Tris/Glycine, amino acid buffers | Tris-HCl, Tris/Glycine, amino acid buffers | Tris-HCl–based, amino acid buffers |
| Features | Micelles of anionic surfactants contained in the running buffer bind to proteins, increasing their solubility and imparting a net negative charge to the entire complex. This allows electrophoretic separation according to molecular weight, independent of the isoelectric point (pI). The band resolution is reported to be higher than that of BN-PAGE. | When large amounts of negatively charged Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) bind to proteins, their solubility is enhanced and the entire complex becomes negatively charged, enabling electrophoretic separation regardless of pI. Hydrophobic proteins bound to CBB remain stable without aggregation and are not dissociated by surfactants. In contrast, basic water-soluble proteins that do not bind CBB cannot be separated by this method. | Protein migration strongly depends on protein charge and isoelectric point. Negatively charged proteins (acidic proteins with a pI lower than the gel environment) migrate toward the anode, whereas positively charged proteins (basic proteins with a pI higher than the gel environment) migrate toward the cathode and may disappear. In some cases, proteins may precipitate during electrophoresis, resulting in smeared band patterns. | This system can be used for native electrophoresis of both proteins and DNA. In polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the mobility of both protein and DNA bands is increased, allowing clearer separation of low–molecular-weight bands. In particular, DNA fragments of 10–20 bp, which are typically difficult to resolve, can be clearly separated even on 15% gels. |
| Running Buffer / Gel Color | Clear | Dark blue (derived from CBB) | Clear | Clear |
| In-gel Enzymatic Activity Assay | Since protein denaturation is minimized, enzymatic activity is preserved. It is widely used for measuring the activities of OXPHOS, ATP synthase, NADPH-related enzymes, HRP, and various other enzymes. | Enzymatic activity may be inhibited due to binding of CBB. In addition, staining of the gel and proteins may interfere with the detection of enzymatic activity. | As protein denaturation does not occur, enzymatic activity is preserved. However, precipitation or reverse migration may occur during electrophoresis, sometimes preventing clear band separation. | Since protein denaturation does not occur, enzymatic activity is preserved. |
| ◎ | △ | ○ | ○ | |
| In-gel Fluorescence Assay | Since protein denaturation is minimized, fluorescence reactions are not inhibited, and absorption of fluorescent signals does not occur due to the clear background. It is used for analysis of Cy-dye–labeled proteins, GFP, YFP, and other fluorescent proteins. | Fluorescence detection may be inhibited because CBB binds to proteins. In addition, strong blue staining of the gel and proteins interferes with fluorescence detection by absorption, and fluorescence quenching of approximately 90–95% has been reported. | Since protein denaturation is minimized, fluorescence reactions are not inhibited, and absorption of fluorescent signals does not occur due to the clear background. However, precipitation or reverse migration may occur during electrophoresis, sometimes preventing clear band separation. | Since protein denaturation is minimized, fluorescence reactions are not inhibited, and absorption of fluorescent signals does not occur due to the clear background. |
| ◎ | △ | ○ | ○ | |
| Protein complex analysis | Because a small amount of an anionic surfactant is included, unstable interactions between subunits may dissociate during electrophoresis. As a result, some protein complexes may not be separated at their intact size. | Since dissociation of complexes does not occur during electrophoresis, complexes can be separated easily even in small amounts. This method shows high correlation with chromatography (≥90%) and is widely used for analysis of OXPHOS, ATP synthase, GPCRs, membrane proteins, and other protein complexes. | Although complex dissociation does not occur during electrophoresis, precipitation or reverse migration may occur, sometimes preventing clear band separation. | Complex dissociation does not occur during electrophoresis and this system is more suitable for separation of low–molecular-weight complexes than high–molecular-weight complexes. |
| △ | ◎ | △ | △ |
ATTO Electrophoresis Buffer Selection Guide
| Application | Running Buffer | Gel Buffer | Applicable Gels | Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Protein | DNA | DNA | |||||
| Method | SDS-PAGE | Native-PAGE | DNA-PAGE | DNA-PAGE | Hand made Gels | ATTO Precast Gels | Agarose Gel | |
| AE-1411 EzRun | 〇 | - | - | - | 〇 Tris-based and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | - | A general-purpose Tris/Glycine/SDS running buffer compliant with the Laemmli method. Low cost; supplied as a powder for long-term storage. |
| AE-1412 EzRun C+ | 〇 | - | - | - | 〇 Tris-based and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | - | Contains reducing agents to suppress band broadening caused by re-oxidation during electrophoresis, enabling sharp band separation. Supplied as a powder. |
| AE-1415 EzRun T | 〇 | - | - | - | 〇 Tricine-based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 p-PAGEL, cp-PAGEL Neo | - | Tris/Tricine/SDS buffer for Tricine PAGE, suitable for separation of peptides and low–molecular-weight proteins. |
| WSE-7050 EzRun TAE | - | - | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | Gel buffer / running buffer mainly used for DNA separation on agarose gels. | ||
| WSE-7051 EzRun TBE | - | - | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 TBE-based, Tris-based, and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | 〇 | Gel buffer / running buffer mainly used for DNA separation. Can be used with both agarose gels and polyacrylamide gels. |
| WSE-7055 EzRun TG | - | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 Tris-based and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | - | Tris/Glycine buffer without SDS. Compatible with Native-PAGE for proteins and DNA. Enables BN-PAGE of proteins when supplemented with WSE-7067 EzBlueNative Additive. |
| WSE-7056 EzRun ClearNative | - | 〇 | - | - | 〇 Tris-based and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | - | High-resolution Clear Native PAGE running buffer without SDS. Uses an anionic surfactant to minimize electrophoretic interference, allowing efficient separation of native (non-denatured) proteins. |
| WSE-7057 EzRun BlueNative | - | 〇 | - | - | 〇 Tris-based and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | - | Blue Native PAGE running buffer without SDS. Supplied with EzRun BlueNative Additive. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) enables separation of native protein complexes without dissociation while minimizing electrophoretic interference. |
| WSE-7065 EzRun MOPS | 〇 | - | - | 〇 Bis-Tris–based, imidazole-based, Tris-based, and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | - | Tris/MOPS/SDS buffer compatible with various polyacrylamide gels. Reduces protein mobility, improving resolution in the low–molecular-weight range. High electrophoretic speed enables rapid separation. |
|
| WSE-7066 EzRun MOPS non-SDS | - | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 Bis-Tris–based, imidazole-based, Tris-based, and Tris/Glycine–based polyacrylamide gels | 〇 e-PAGEL, e-PAGEL HR, u-PAGEL H, c-PAGEL Neo | 〇 | Tris/MOPS buffer without SDS. Compatible with Native-PAGE for proteins and DNA. Enables BN-PAGE of proteins when supplemented with WSE-7067 EzBlueNative Additive. |
ATTO Blotting Reagent Selection Guide
| Application | Semi dry Blotting Reagents | Tank Blotting Reagents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | WSE-4056/57/58 QBlot kit C/M/W | WSE-7210 EzFastBlot HMW | AE-1465 EzFastBlot | AE-1460 EzBlot | WSE-7055 EzRun TG | WSE-7055 EzRun TG |
| Ease of Use / Operability | ★★★★★ (Transfer Pack) | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
| Transfer Time | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
| Transfer Efficiency | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| High-Molecular-Weight Proteins | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| After Native-PAGE | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Molecular Weight Range | 10~250kDa | 15~600kDa | 20~250kDa | 20~250kDa | 20-100kDa | 15~200kDa |
| Transfer Conditions (Fast) | 5-20min (24V) | 5-30min (24V) | 5-20min (24V) | - | - | 60min (150V) |
| Transfer Conditions (Standard) | 30-60min (12V) | 60min (12V) | 60min (12V) | 60min (12V) | 60min (2mA/cm 2 ) | O/N(25 V) |
Brochure
Instruction Manual
Specifications
| WSE-7056 EzRun ClearNative | |
|---|---|
| Components | ① Cathode buffer: Tris, anionic surfactant ② Anode buffer: Tris |
| Volume | ① Cathode buffer (5×): 500 mL ② Anode buffer (5×): 500 mL |
| Usage | Dilute 5-fold with distilled water |
| Storage / Shelf Life | Store at room temperature for 1 year |
Ordering Information
| Code No. | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| 2332313 | WSE-7056 EzRun ClearNative | 1 pk |